Read the latest news on TAWNY's events, projects, publications, and other achievements.

Presented at the "Kongress der Deutschen Marktforschung 2025"
Marktforschung mit Vision AI: Neue Formen zur Erfassung der CX bei Live-Events
Kongress der Deutschen Marktforschung 2025
Video Analytics als neue Datenquelle: Neue Formen zur Erhebung der Customer Experience bei Live-Events durch Applied AI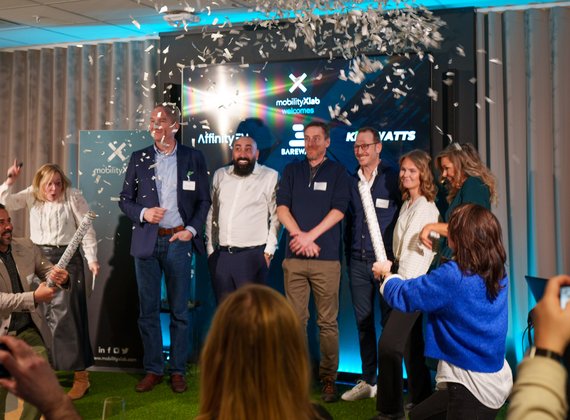
MobilityXLabs
TAWNY changes the way you drive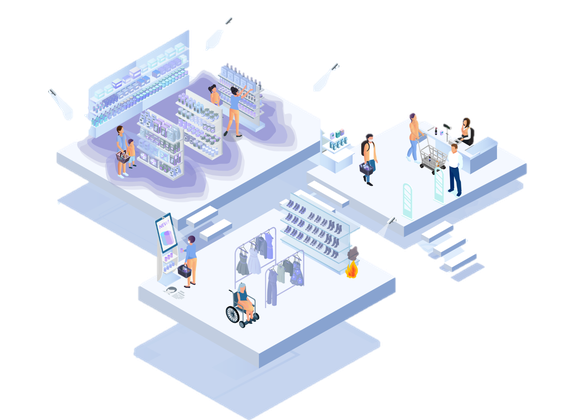
Tech For Retail 2024
TAWNY Inside: A Successful Debut at Tech For Retail in Paris
AI outlook
BETWEEN TECHNOLOGY & HUMANITY: HOW EMOTION AI TRANSFORMS MEDIA AND SOCIETY
SODEXO
BETWEEN TECHNOLOGY & HUMANITY: HOW EMOTION AI TRANSFORMS MEDIA AND SOCIETY
Vision AI in Retail
Transforming Experiences in Retail and Beyond
EuroCIS 2024
Exploring the Future of Retail Analytics
Live Matters
Collaboration announcement: TAWNY enters the field of audience analytics
MediaMarkt
TAWNY's Entry into Retail Market: An Update from the Media Markt Tech Challenge
Marktforschung.de
Interview: Decoding customer experience with Vision AI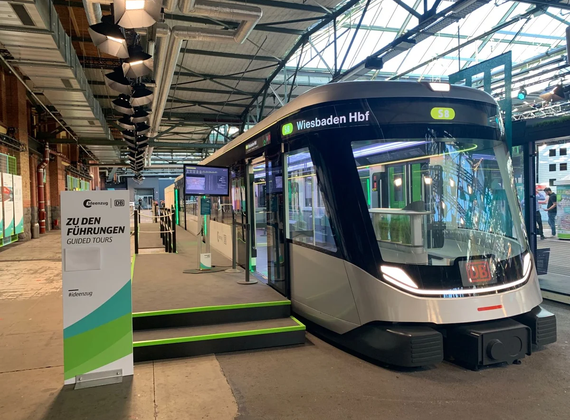
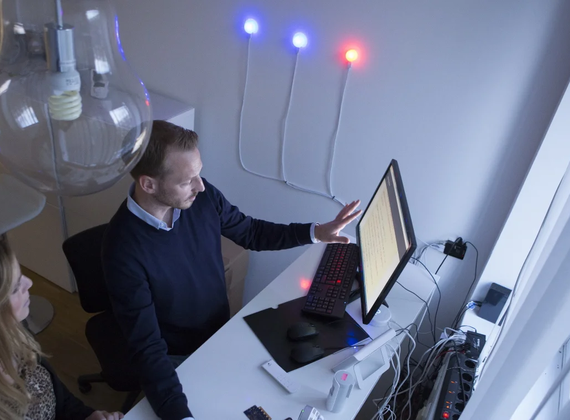
Deutsche Bahn
Zukunft Nahverkehr 2023: TAWNY presents its prototype for DB Regio
IAA
Meet TAWNY at IAA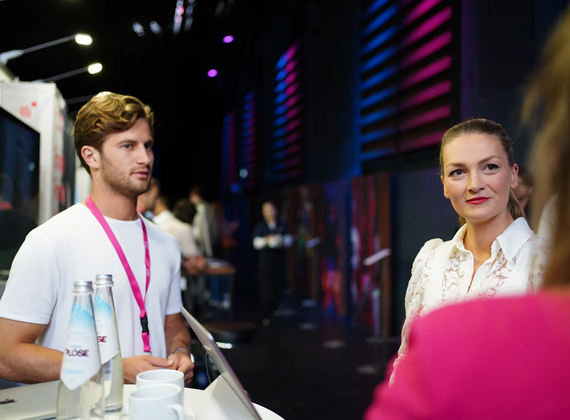
Tech Days
TAWNY at Tech Days 2023 in Munich
Woche der Marktforschung
Webinar: The Future of Digital Shelf Testing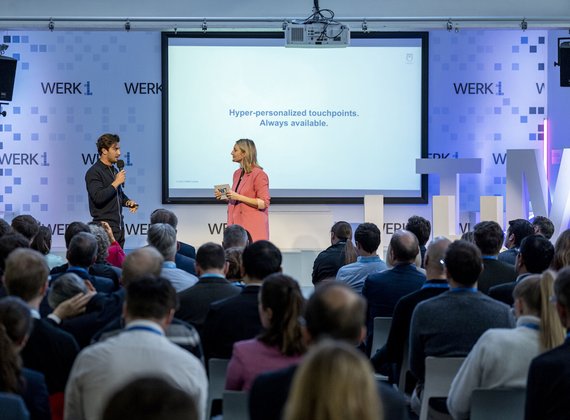
InsurTech Hub Munich
Smart, empathetic, and hyper-personalized customer touchpoints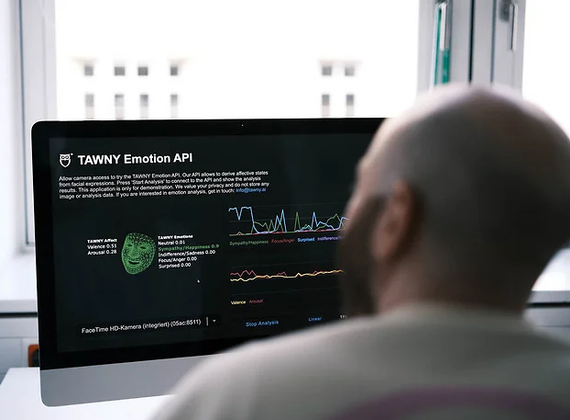
Ad Skip
New study: AI predicts ad skipping
Memories That Make Us
User study: What makes a lasting memory?
Published: Absatzwirtschaft
Neuro Marketing: new article published
Market Research Award 2022
TAWNY receives the German Market Research by BVM
EROC
TAWNY x [m]SCIENCE: Testing Emotional Reactions on Creatives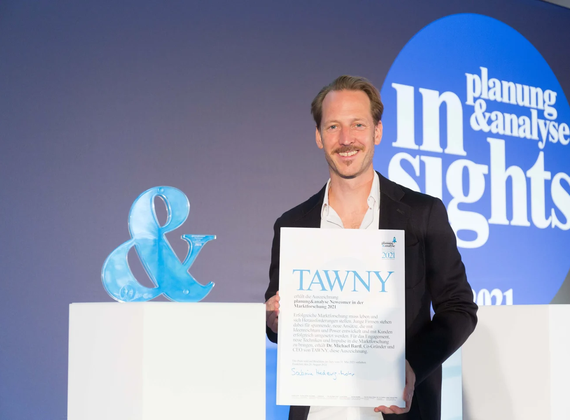
planung&analyse
Newcomer in Market Research 2021
SAP.io Foundry
TAWNY will be part of the SAP.io cohort in Fall 2020
New Work
Project Update: Working in Flow @ Siemens
The Force AI
TAWNY joins forces with LEGO® Star Wars™ for cinema promotions
The Missing Piece
Decoding Human Flow at the Workplace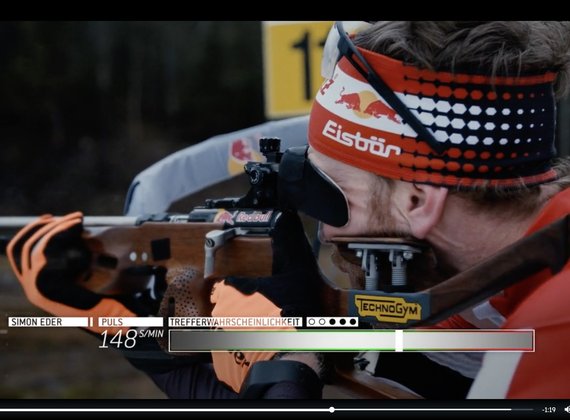
Biathlon meets Emotion AI
From Lenzerheide to Tyrsil: detecting the DNA of flow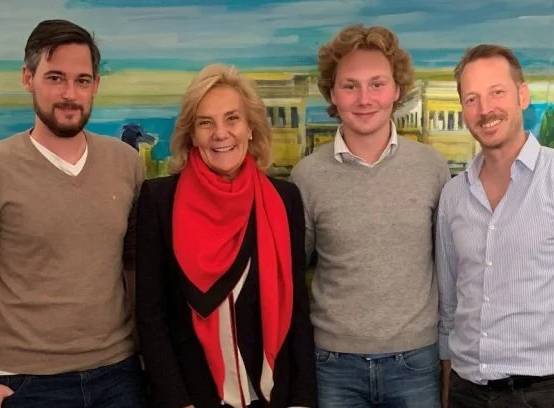
Meet our Angels
Susanne and Felix Porsche invest in Deep Tech Startup TAWNY
Horizon 2020
TAWNY receives Horizon 2020 funding
Handelsblatt AI Conference
TAWNY wins at the Handelsblatt AI ConferenceDIGICON 2016
Digitale Welt Convention
