Our solutions are developed and tested with established partners and clients in various fields of application. Don't hesitate to reach out if you can't find the use case you're looking for. TAWNY's extensive cross-industry experience enables us to tailor solutions to your unique challenge.

Market Research
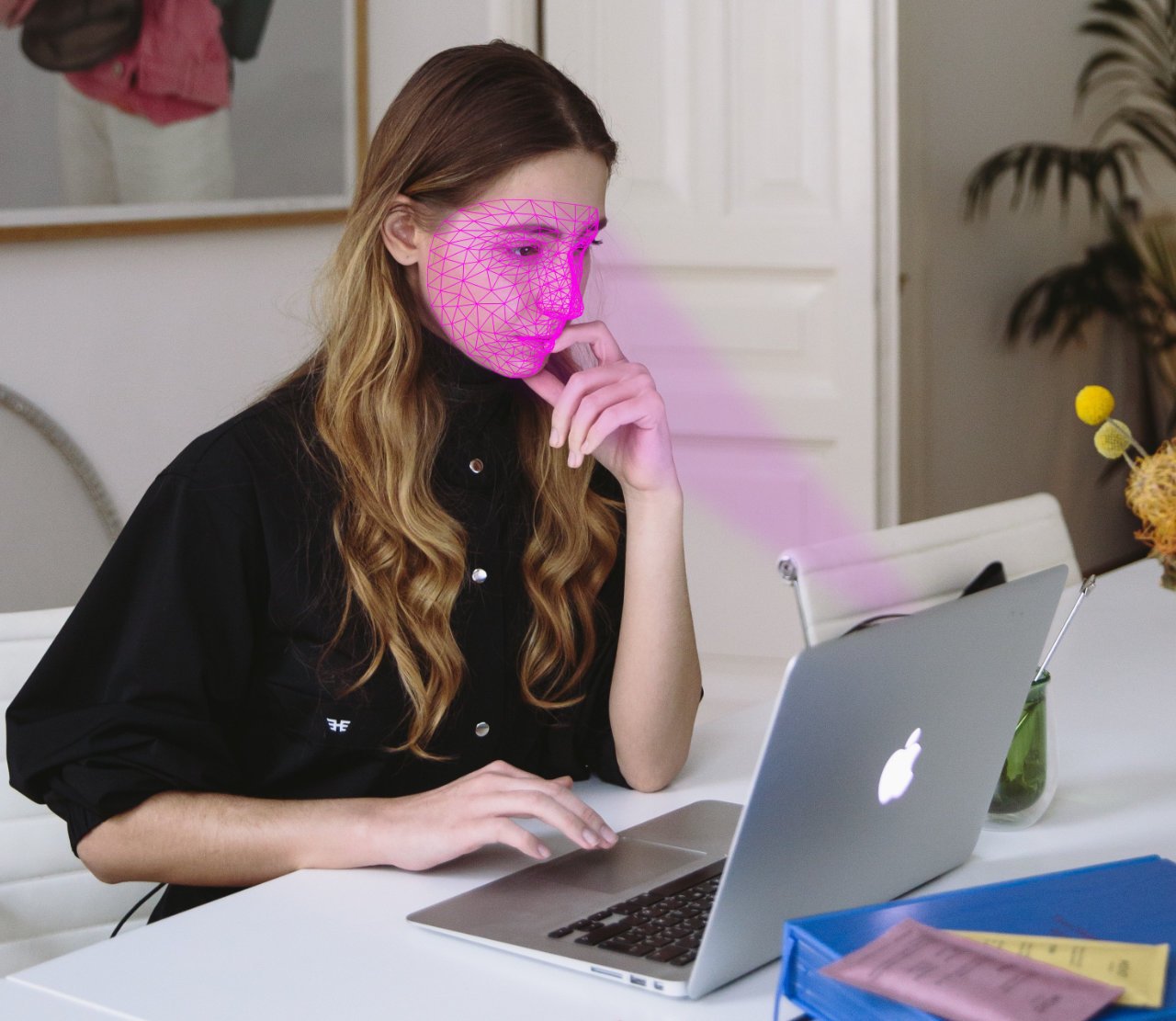
Our innovative approach to market research leverages Emotion AI and web-based eye tracking, transforming participants' homes into digital labs. These technologies allow for in-depth analysis of consumer responses to advertising, UX design, and product offerings. Additionally, we offer a video recording tool to capture participant reactions, enriching our data collection.
The integration of Emotion AI enables us to understand emotional responses to marketing stimuli, while web-based eye tracking provides insights into visual attention and engagement. This combination not only enhances the accuracy of our research but also makes emotion detection and eye tracking more affordable and accessible. Our methods offer a cost-effective solution for gathering comprehensive consumer insights, facilitating more effective marketing strategies and product development.






Transportation
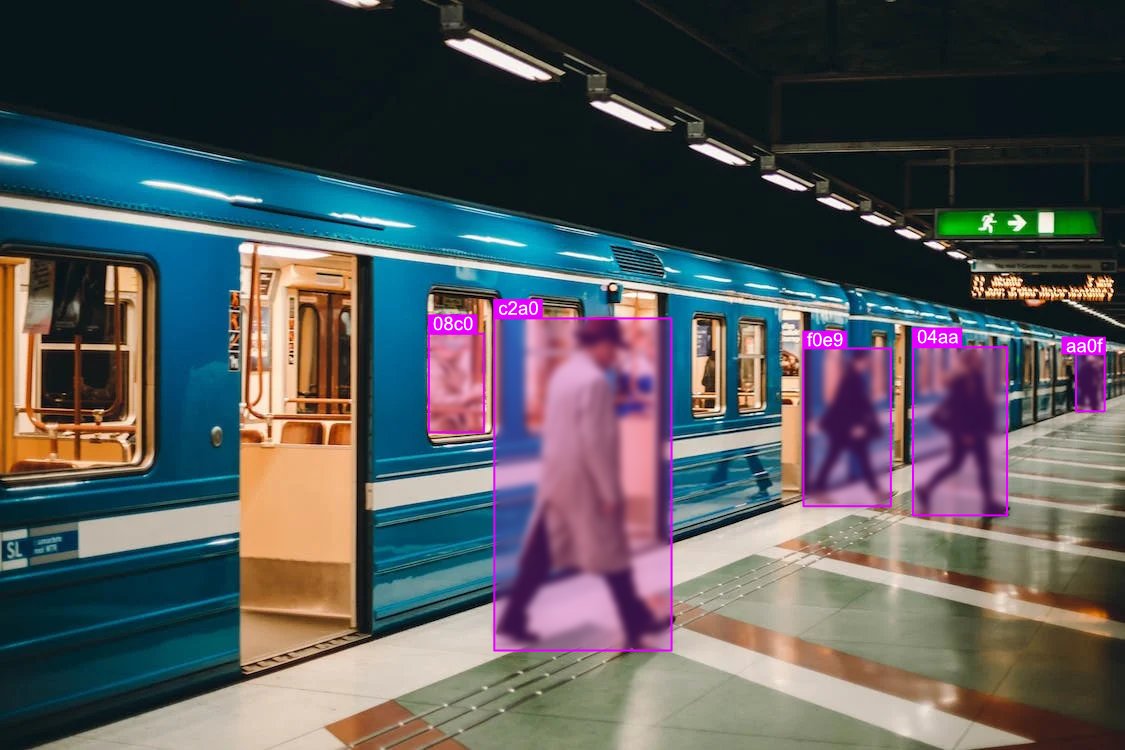
In our cooperation with Deutsche Bahn (DB Regio), we've successfully customized TAWNY's cutting-edge crowd analytics technology. Our collaboration led to the development of an innovative system for automated passenger counting 2.0, a significant advancement in the field of public transportation.
This state-of-the-art system utilizes existing cameras and customized AI algorithms with the objective of accurately counting and analyzing passenger flow in real-time. By integrating this technology into a transportation network, we will enable more efficient management of passenger volume, leading to enhanced service planning and optimized resource allocation.
The data gathered through the 'passenger counting system 2.0' offers numerous opportunities. It allows for better prediction of peak travel times, improving scheduling and reducing overcrowding. Additionally, it aids in maintaining safety standards by monitoring and managing passenger density. This innovative approach not only enhances passenger experience but also supports commitment to sustainable and efficient public transportation.
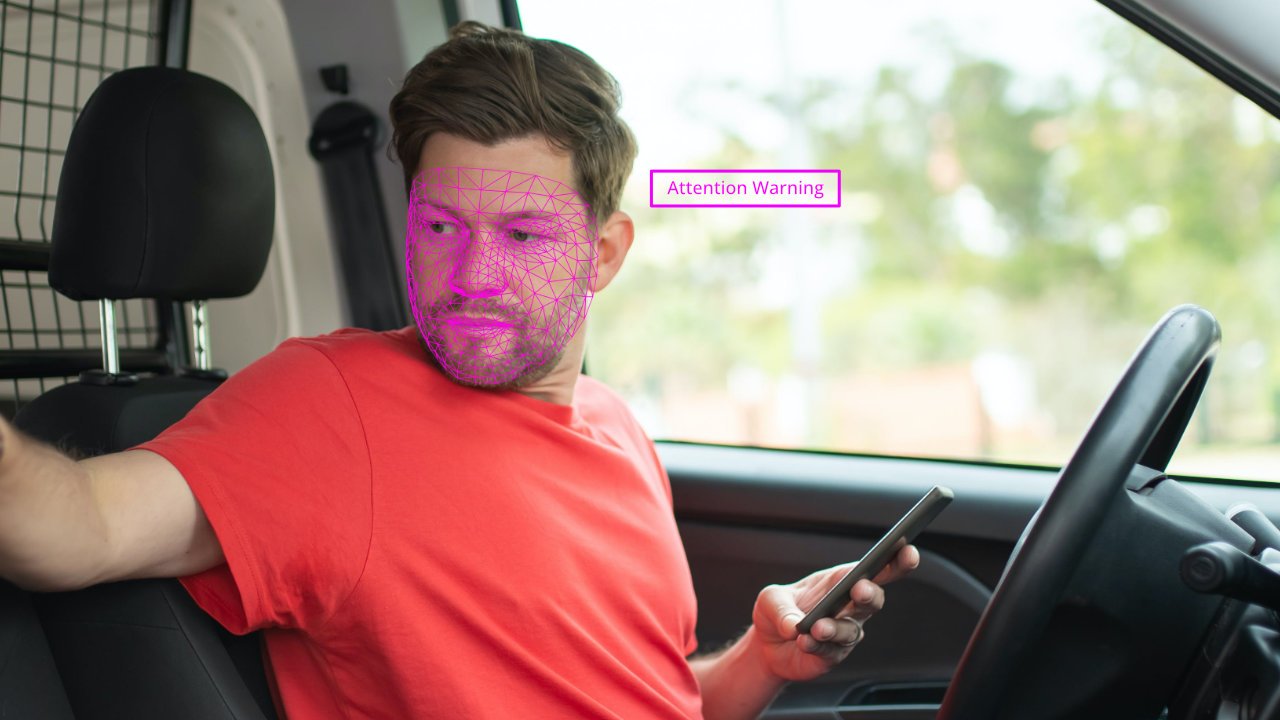


Automotive
Vision AI is revolutionizing interior monitoring in cars, ushering in a new era of safety, comfort, and personalized driving experiences. Equipped with advanced cameras and intelligent algorithms, Vision AI systems are adept at monitoring the car's interior in real-time. These systems can detect and analyze driver behavior, ensuring alertness and mitigating potential distractions.
Facial recognition technology allows for personalized settings, adjusting preferences like seat positions and climate control based on individual drivers. Interior monitoring extends to passenger safety, with the ability to identify and alert about unattended items or the presence of occupants, ensuring a secure environment.
Furthermore, Vision AI contributes to enhancing in-cabin entertainment experiences by recognizing gestures and expressions, allowing for hands-free control. In the realm of automotive innovation, interior monitoring with Vision AI is a cornerstone, elevating both safety and user satisfaction within the confines of the vehicle.
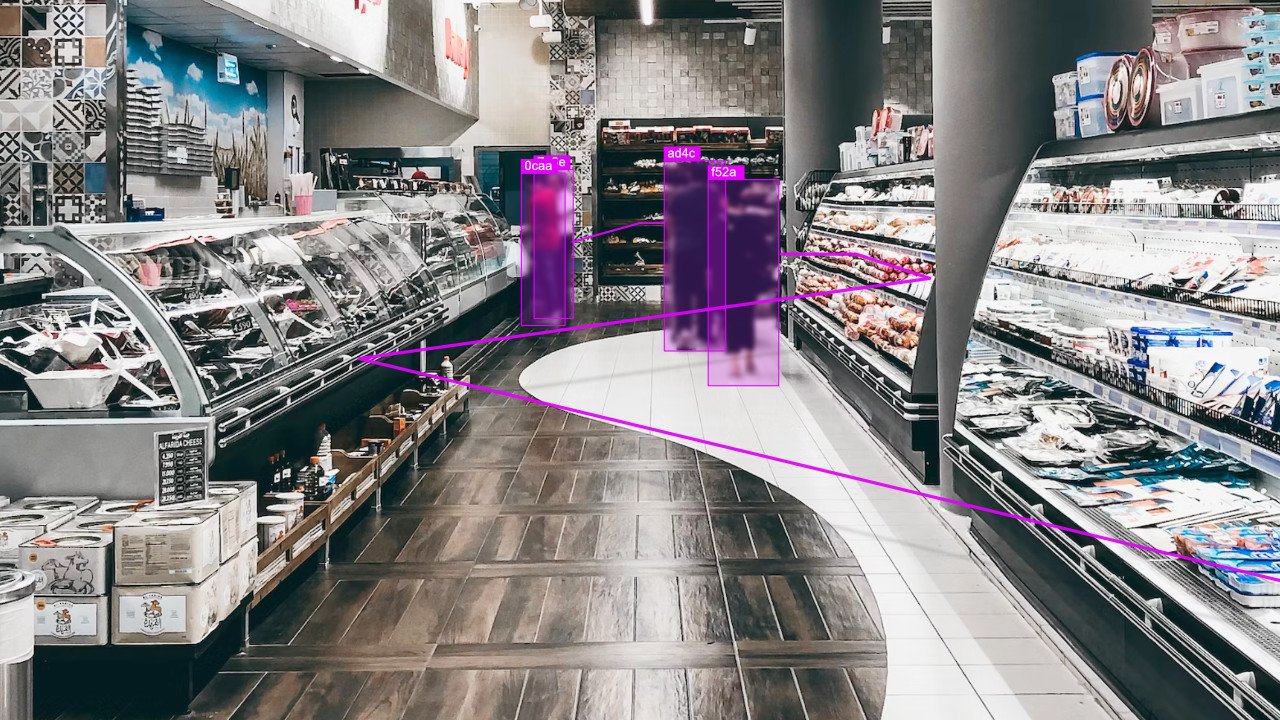



Retail
Vision AI technology is reshaping the landscape of retail by offering insightful solutions to enhance customer experiences and operational efficiency. Utilizing advanced computer vision algorithms and existing camera systems, crowd analytics provides retailers with a detailed analysis of customer behavior, foot traffic patterns, and popular shopping areas. This data empowers retailers to optimize store layouts, strategically place products, and enhance overall in-store experiences.
Moreover, Vision AI contributes to personalized marketing strategies by tracking customer preferences and behaviors, enabling retailers to tailor promotions and recommendations. It proves instrumental in managing queue lengths at checkout counters, reducing wait times, and ultimately improving customer satisfaction.
In the retail sector, crowd analytics stands as a powerful tool that not only drives sales but also enables businesses to adapt and innovate based on real-time insights into consumer dynamics.
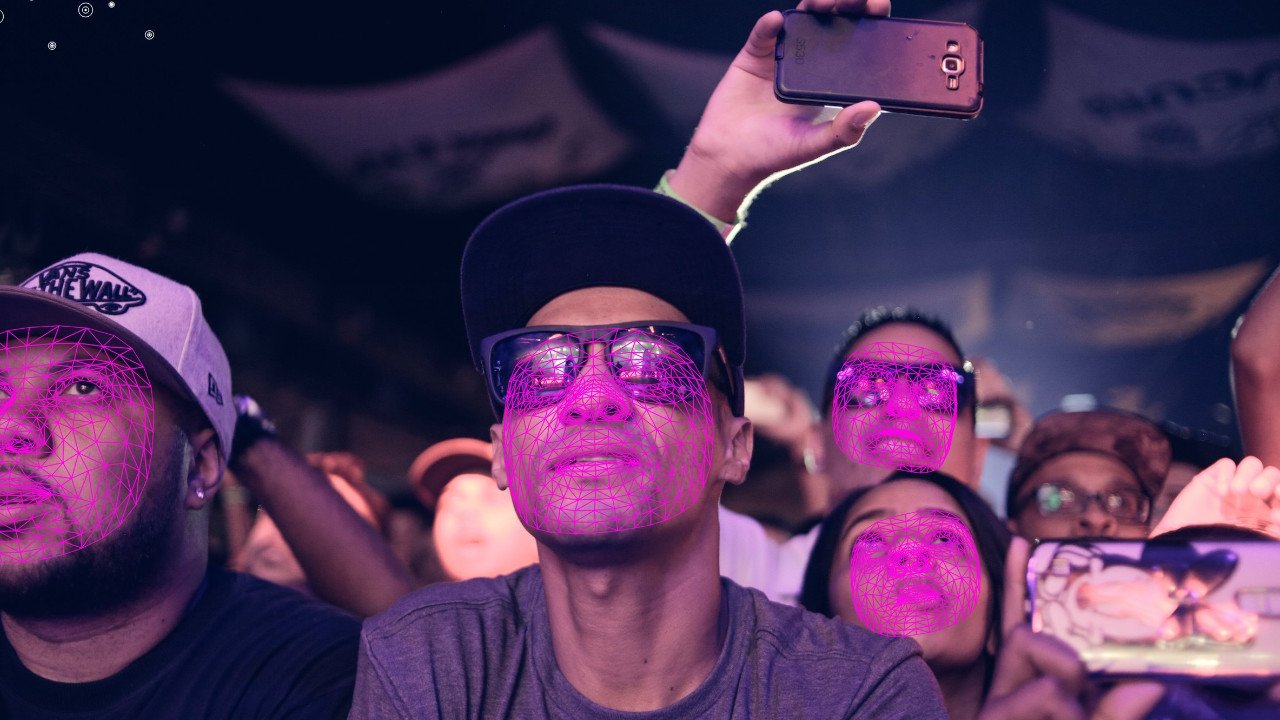

Entertainment
Crowd analytics technology is revolutionizing event management by providing a comprehensive and real-time understanding of crowd dynamics. Through the deployment of cameras and advanced computer vision algorithms, event organizers can monitor crowd size, movement patterns, and density, enabling them to make informed decisions to enhance safety, security, and overall participant experience.
Crowd analytics facilitates efficient crowd flow management, allowing organizers to identify potential congestion points and optimize event layouts. Additionally, the technology contributes to security measures by quickly detecting anomalies or potential risks within the crowd.
From music festivals to sporting events, crowd vision is a valuable tool that empowers organizers to create safer, more enjoyable, and well-organized experiences for attendees, while also providing insights for future event planning and logistics.



Scientific Research
We are at the forefront of pioneering scientific research, harnessing the power of emotion measurement to elevate your research methodologies. Move beyond the limitations of traditional data collection methods like self-reporting, observation, and interviews, and embrace the innovation of emotion analytics.
Our approach involves the seamless integration of video recordings into your experimental setup, transforming data collection into a dynamic and insightful process. This method allows for the conversion of your participants' homes into interactive labs, offering a more natural and authentic environment for data gathering.
Utilizing the TAWNY Emotion Analytics Platform, you gain direct access to raw emotion data, conveniently provided in a .csv file format. This flexibility allows you to conduct thorough statistical analysis using your preferred tools, such as R, Python, or SPSS, to name a few.
To showcase the effectiveness and versatility of TAWNY's technology, we have compiled a collection of research projects that have successfully utilized our platform.